Adapter Pattern
05 Aug 2020
Contents
What is Adapter Pattern?
Adapter pattern lets the interface of an existing class to be used as another interface, and it makes existing classes work with others without modifying them.
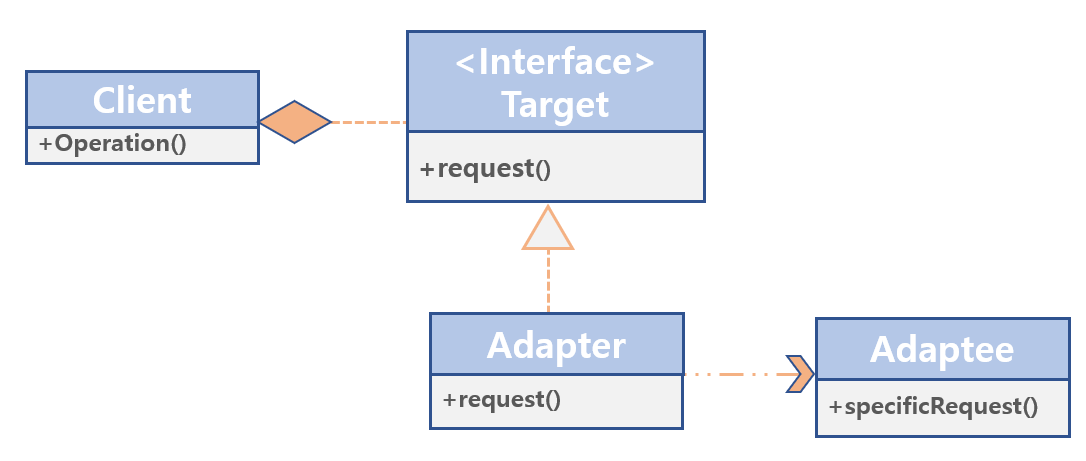
Client: Client calls method using target interface. The client sends a request to the adapter through the Target Interface.Target: Interface that adapter implements.Adapter: Implements the target interface in terms of adaptee. Responsible for connecting the client and adaptee, which are not compatible..Adaptee: Third-party library or external system. All request are delegated to the adaptee.
Adapter Pattern is a pattern that converts the interface of one class into another interface that client want to use.
Adapter patterns helps troubleshoot compatibility issues with other interfaces.
Why use Adapter Pattern?
- Adapter is also available to use in all subclasses of adaptee.
- Connect the client to the interface, not to a specific implementation.
- It allows existing classes to be reused in compatibility with other interface.
As an example of real life, you can often see every country uses different plugs when you travel abroad. Therefore, in order to charge a smartphone, it is necessary to use a charging cable suitable for the plug or to use an adapter. Adapter pattern also connect something that is not compatible like this.
The battery can be charged if there is a cable according to the type of usb and a port suitable for the cable.
First, the cable must be connected (connectCableC) to start charging the battery (chargeBatteryC).
public interface USBCtypeCable {
public void connectCableC();
public void chargeBatteryC();
}
public class CtypePortBattery implements USBCtypeCable {
@Override
public void connectCableC() {
System.out.println("Connected with USB Type-C cable.");
}
@Override
public void chargeBatteryC() {
System.out.println("USB Type-C battery is now charging.");
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CtypePortBattery batteryC = new CtypePortBattery();
System.out.println("[USB Type-A Battery]");
batteryC.connectCableC();
batteryC.chargeBatteryC();
}
}
But what if you only have a USB TYPE-A cable and you have to charge the battery having Type-C port? You will have to use an adapter at this time.
Pros and Cons
There are Object adapter and Class adapter.
Object Adapter
- It is more flexible because it uses a composition rather than inheritance.
- But,
Adapteeobject must be created for use.
Class adapter
- Adaptee’s behavior can be overridden because Adapter is a subclass of Adaptee.
- And, do not need to create Adaptee objects.
- But, because inheritance is used, one adapter class is applicable only to a particular adaptee class.
- Also, only available in languages with multiple inheritance support.
Example
Cable and battery
- USB Type-A Cable
- USB Type-A Port Battery
- USB Type-C Cable
- USB Type-C Port Battery
USB Type-A Port Battery requires usb type-A cable, and USB Type-C Port Battery requires usb type-C cable.
First, create two cable interfaces USBAtypeCable and USBCtypeCable.
public interface USBAtypeCable {
public void connectCableA();
public void chargeBatteryA();
}
public interface USBCtypeCable {
public void connectCableC();
public void chargeBatteryC();
}
The battery with usb type-A port implements the interface USBAtypeCable. And, the battery with usb type-C port implements the interface USBCtypeCable.
public class AtypePortBattery implements USBAtypeCable {
@Override
public void connectCableA() {
System.out.println("Connected with USB Type-A cable.");
}
@Override
public void chargeBatteryA() {
System.out.println("USB Type-A battery is now charging.");
}
}
public class CtypePortBattery implements USBCtypeCable {
@Override
public void connectCableC() {
System.out.println("Connected with USB Type-C cable.");
}
@Override
public void chargeBatteryC() {
System.out.println("USB Type-C battery is now charging.");
}
}
We should charge the battery with usb type-C port by using usb type-A cable. Therefore, make the adapter so that the battery can be charged.
public class USBadpater implements USBAtypeCable {
USBCtypeCable usbCtypeCable;
public USBadpater(USBCtypeCable usbCtypeCable) {
this.usbCtypeCable = usbCtypeCable;
}
@Override
public void connectCableA() {
usbCtypeCable.connectCableC();
}
@Override
public void chargeBatteryA() {
usbCtypeCable.chargeBatteryC();
}
}
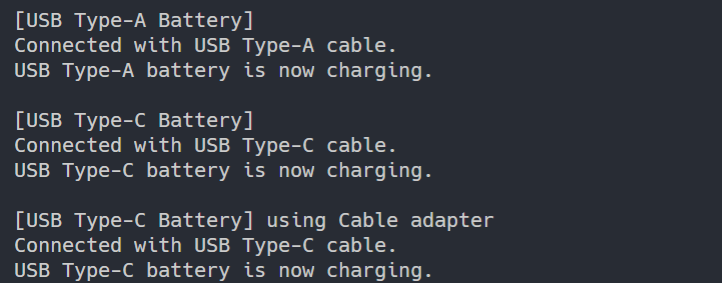
Finally, let’s test that the battery is being charged well.
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtypePortBattery batteryA = new AtypePortBattery();
CtypePortBattery batteryC = new CtypePortBattery();
System.out.println("[USB Type-A Battery]");
batteryA.connectCableA();
batteryA.chargeBatteryA();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("[USB Type-C Battery]");
batteryC.connectCableC();
batteryC.chargeBatteryC();
System.out.println();
USBAtypeCable usbAdapter = new USBadpater(batteryC);
System.out.println("[USB Type-C Battery] using Cable adapter");
usbAdapter.connectCableA();
usbAdapter.chargeBatteryA();
}
}