Difference between Register and Memory
09 Jul 2020
Contents
Role of Register and Memory
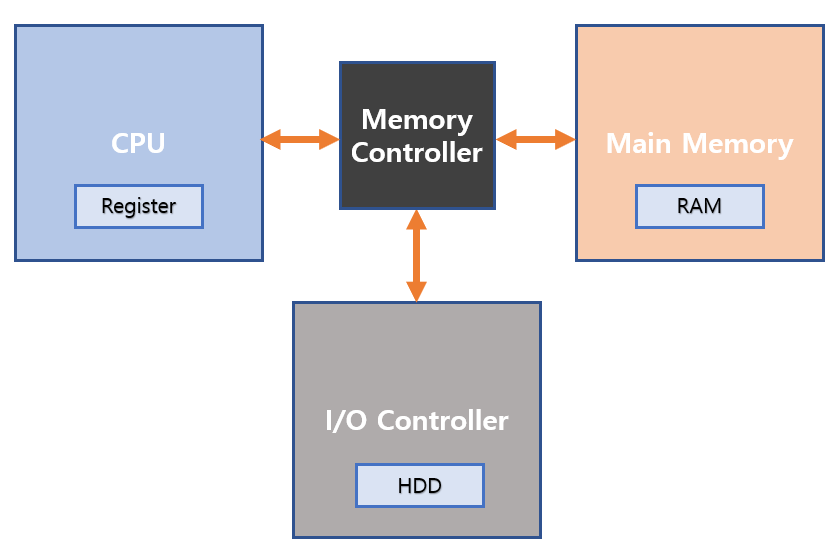
Register and memory hold data that processors can directly access, and this increases the processing speed of CPU.
The processing speed of the CPU can also be increased by increasing the number of bits of the register or the number of physical registers on the CPU. Also, the larger the memory, the better the CPU’s processing speed.
What is Register?
The register is the smallest data holding device embedded in the processor itself.
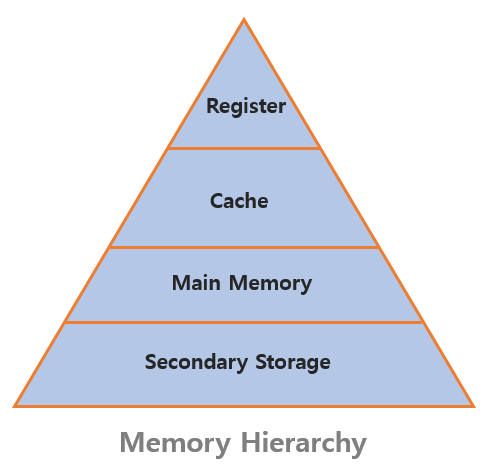
The register resides at the top of the memory hierarchy and processor can access directly. The register holds the instruction or operand that the CPU is currently accessing.
The register is very fast because the CPU has direct access. However, much data cannot be stored because the capacity is very small (16 bits, 32 bits, and 64 bits.). The number of register bits specifies the speed and power of CPU. For example, 32-bit register can access the 32-bit instructions at a time.
What is Memory?
Memory is a primary memory that holds program instruction and data that the program requires for execution.
Memory can also be categorized on the basis of volatile and non-volatile memory. RAM is primary-volatile memory. This means that data is stored temporarily. So, when the power is turned off, the data of the memory loses. ROM is a non-volatile memory in which keeps its data when power turned off.
The primary memory contains the data that will be required by the currently executing program in CPU. If the data needed for processor is not in memory, it is sent from the secondary storage(HDD,SSD) to primary memory and then the data is imported by the processor.
The capacity of memory is GB or more. The larger the memory, the better the computer’s performance. Ram can store a lot of data because of its large capacity, but it is slower than the register.