Synchronous and Asynchronous
27 Jul 2020
Contents
- Synchronous and Asynchronous
- What is Synchronous?
- What is Asynchronous?
- Blocking and Non-blocking
- Four Cases
Synchronous and Asynchronous
Two ways to send, receive, and reply data, Synchronic and Asynchronous.
Synchronous means connected or dependent. Asynchronous means independent.
What is Synchronous?
If we request something, the results must be given at the request no matter how long it takes.
RequestandResultoccur simultaneously.
Synchronous processing model is very simple to design and intuitive, but there is a disadvantage that have to wait until the results are given. We can do nothing while we wait.
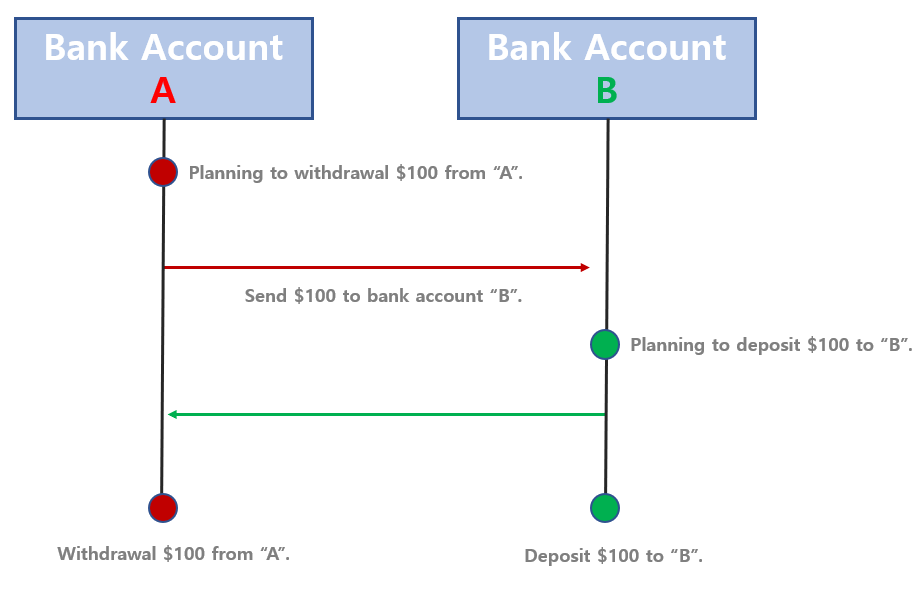
For example, transferring money would be more appropriate using synchronous processing model.
Suppose we withdraw money from bank account A and send it to bank account B.
- First, we need to plan to withdrawal $100 from
A. - Then, send $100 to bank account
B. - Account
Brecognizes that he received $100, thenBreply toAthat he received $100. - Finally, the money is decreased from account
Aand increased from accountBat the same time.
What is Asynchronous?
If we request something, the results does not given at the request.
Requestandresultnot occur simultaneously.
Asynchronous processing model is complicated, but even if it takes time to get results, we can do other things during that time, so we can use resources efficiently.
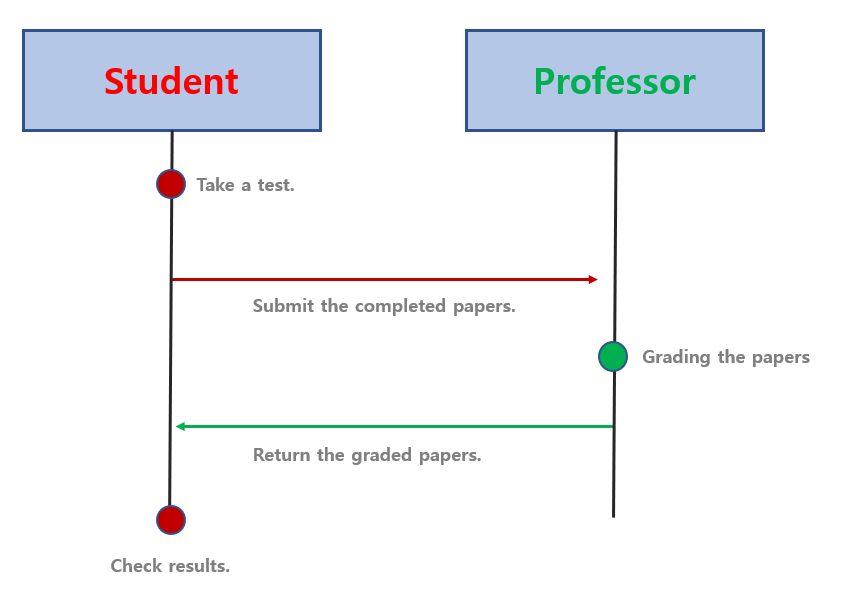
Let’s think we should take an exam at the College.
- First, students need to take a test.
- Then, submit the completed papers.
- Professor grades the papers.
- Then, return them to students.
- Finally, students will check the results.
Students and professors have a link called test papers, but what they did about the test papers is different.
Students solved the test papers and Professors graded the test papers.
Because they have different objectives, their processing times do not match, and they do not have to match.
Blocking and Non-blocking
Blocking
Blocking, if the called function continues to have control and does not return it directly to the called function until it has finished its job.
Non-blocking
Non-blocking, if the called function gives control right away even if the function haven’t finished what he is supposed to do, and the called function allows you to proceed with something else.
Four Cases
1. Synchronous and Blocking
Students will be in a Synchronous and block state if they just wait and do nothing until they receives the papers back after they submitted them.
2. Synchronous and Non-blocking
The last thing students have to do after submitting the test paper is to check the results. So, students will be in a Synchroonus and Non-block state if they keep asking the professor if he’s finished garding the test. Students are not allowed to do anything else, but they are very interested in the professor’s grading being done. (Polling)
3. Asynchronous and Blocking
Students finished their test and submitted it. But suddenly, the professor tells the students not to go home until the grading is complete. Students want to check their scores after they submitted the test, but they just think about that. They are not interested in what the professors are doing. Students just wait grading and wait for their final work checking the results. Therefore, students will be in a Asynchronus and block state (Select)
4. Asynchronous and Non-blocking
If students hand over the test papers and do something else freely until the professor replys that the grading is complete, the student’s status will be Asynchronus and non-block.