What is Singly Linked List?
27 Jun 2020
Contents
What is Singly Linked List ?
- Linked List is a data structure that implements a list using a pointer, so the nodes are ordered linearly.
- The node in the Linked List contains
dataandpointer. - In Singly Linked List, connections between nodes are
one-way. Each node has a connection to to thenext node.
Structure of Singly Linked List
- Connect the first node to be added to the
dummy head node.- It is also possible to implement using a head pointer.
- But, using a head node is easier to implement.
- Use a pointer to connect the newly added node to the previous node.
Advantage of Linked List
- The time complexity of adding and deleting data is O(1).
- Unlike
Array Listthat predicts the number of data to be stored and set the size of the array in advance, data can be added without restrictions on the size of the array. - Memory efficiency is good because it allocates as much memory as necessary data. (
Dynamic memory allocation)
Disadvantage of Linked List
- It takes O(N) to find a data in a particular location.
- No random access is possible, access nodes sequentially. So, it’s not easy to access nth element.
- Implementation is more complex than array list.
- Additional memory for storage is required to store the pointer.
Operations for Linked List
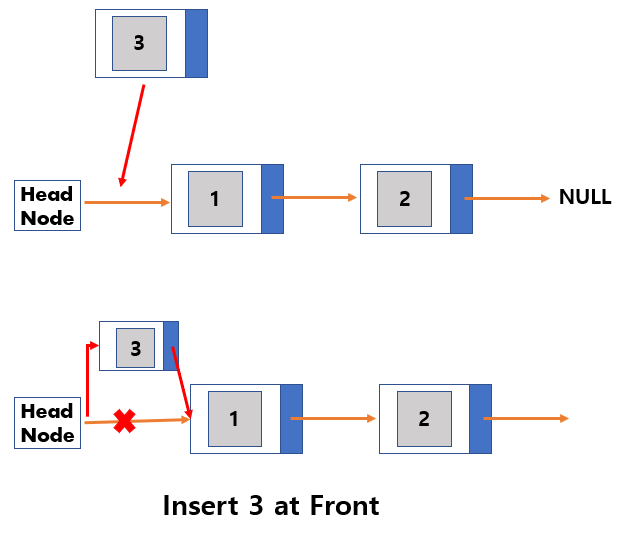
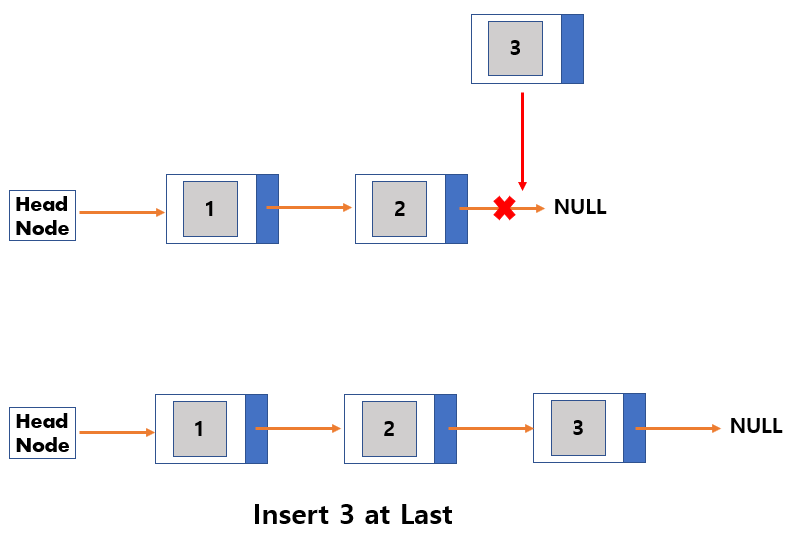
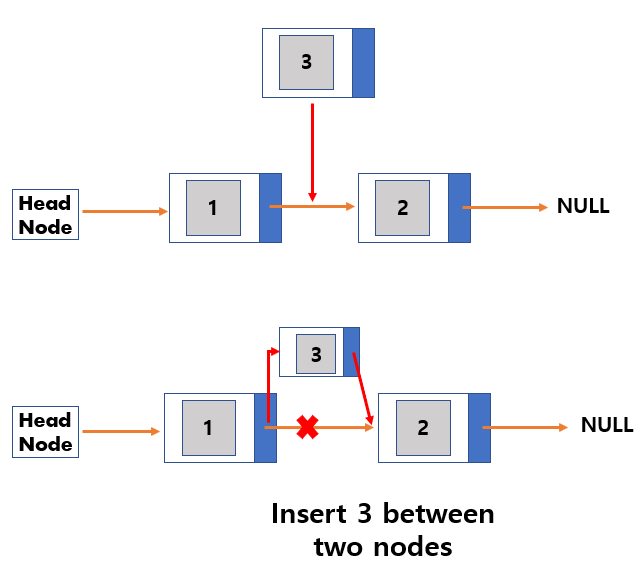
Insertion
- Create New Node to insert.
- Link the newly added node with the next node.
- Link the previous node of the newly added node with the newly added node.
// Make new node and prev node.
// Set the value of the node to insert
pNewNode->data = data;
// "pPrevNode" refers to the previous node in the position to be inserted.
pPrevNode = &(llist->headerNode);
for (i = 0; i < position; i++)
{
pPrevNode = pPrevNode->link;
}
// Connect the "pNewNode" to the next node of "pPrevNode".
pNewNode->link = pPrevNode->link;
// Next node of "pPrevNode" becomes the "pNewNode".
pPrevNode->link = pNewNode;
// Increases the current number of nodes.
llist->currentCount++;
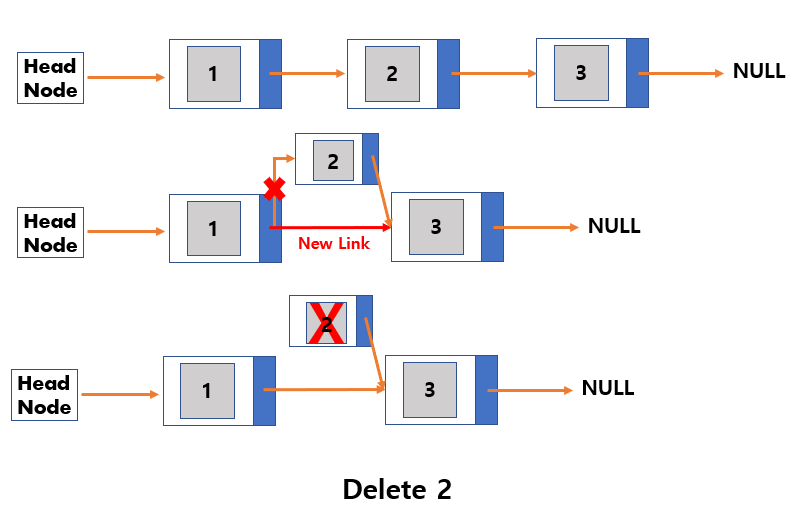
Deletion
- Link the previous node of the node to be removed to the next node of the node to be removed.
- Free the memory of the node to be removed.
// Make del node and prev node.
// "pPrevNode" refers to the previous node in the position to be deleted.
pPrevNode = &(llist->headerNode);
for (i = 0; i < position; i++)
{
pPrevNode = pPrevNode->link;
}
// Specify the node to delete.
pDelNode = pPrevNode->link;
// The next node of "pPrevNode" becomes the next node of "pDelNode".
pPrevNode->link = pDelNode->link
// Remove pDelNode
free(pDelNode);
// Decrease the current number of nodes.
llist->currentCount--;
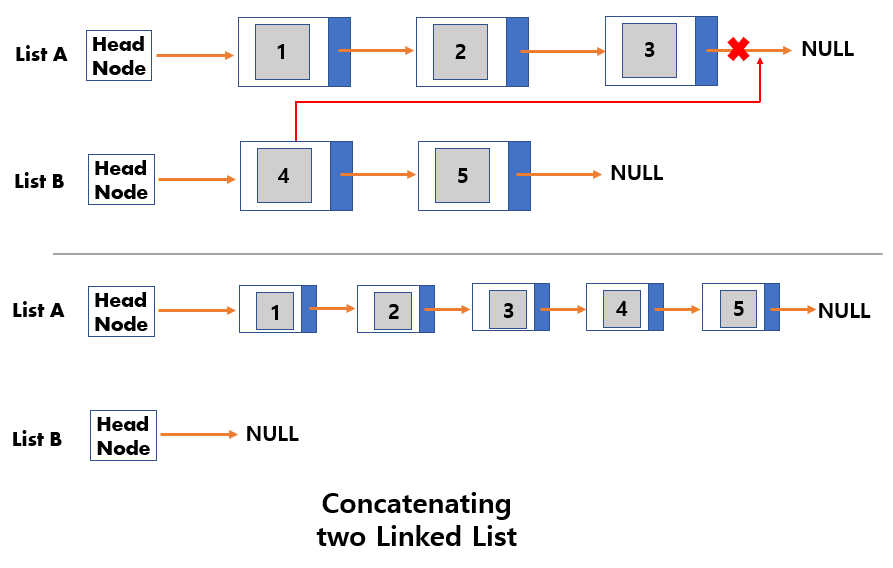
Concatenating two Linked List
- Set
NodeAas the last node inList A,NodeBas the first node inList B. - Connect
NodeAtoNodeB. - Set List B an
empty list.
// Concatenate "pListA" and "pListB".
// "pNodeA" becomes the last node of "pListA".
pNodeA = pListA->headerNode.link;
while (pNodeA != NULL && pNodeA->link != NULL)
{
pNodeA = pNodeA->link;
}
// Set the next node of "pNodeA" as the first node of "pListB".
pNodeA->link = pListB->headerNode.link;
// pListB becomes an empty list.
pListB->headerNode.link = NULL;