Doubly Linked List Implementation
30 May 2020
Contents
What is Doubly Linked List ?
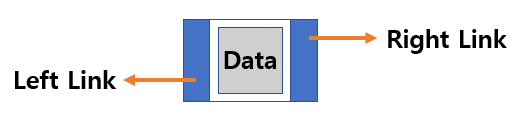
In Singly Linked List, connections between nodes are one-way. However, Doubly Linked List has two-way connections between nodes. Each node has a connection to the previous node as well as a connection to the next node. That is why the Doubly Linked List is accessible to both the previous and the next nodes.
Structure of DDL’s Node
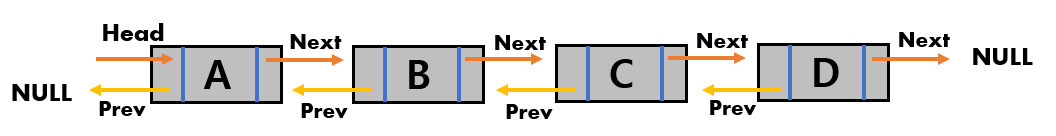
Structure of DDL
Because the first node has no previous node, the link to the previous node is NULL. Also, because the last node has no next node, the link to the next node is NULL.
Advantages of DDL
- Both previous and next accesses are possible.
- You can quickly insert a new node before a given node.
- Deletion is efficient when the pointer of a node to be deleted is given.
- It is fast to explore nodes.
- The Singly Linked List sometimes requires all nodes to be expored when searching for a particular node.
Disadvantages of DDL
- All nodes require additional space for the previous pointer.
- More memory is needed for previous pointer.
- All operations require a previous pointer.
- You have to take care of the previous pointer as well as the next pointer.
Operations
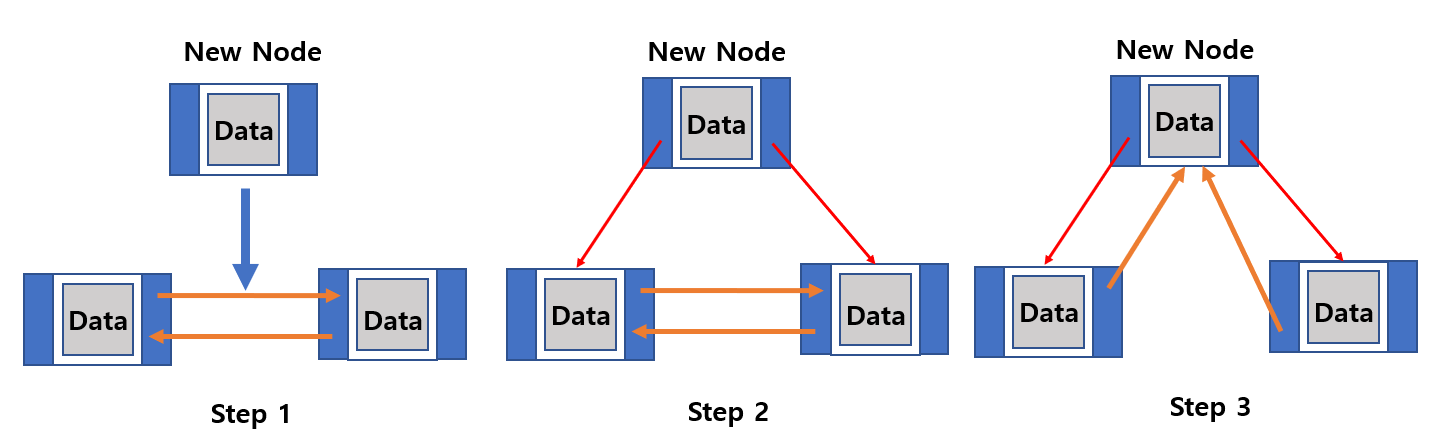
Insert Node
- When adding new data in the DDL, you must create a new node.
- The link between the previous and next node should be connected to the link of the new node.
- Finally, you need to reassign the link of the existing node.
// Set new node to insert.
newNode->data = data;
// prevNode = Previous node of the position to insert new node.
prevNode = &(dlist->headerNode);
for (int i = 0; i < position; i++)
{
prevNode = prevNode->next;
}
// Set the next node of the new node as the next node of the previous node.
newNode->next = prevNode->next;
// Set previous node of new node to prevNode
newNode->prev = prevNode;
// The next node of the prevNode becomes the newNode.
prevNode->next = newNode;
// The previous node of the next node of the newNode is "newNode".
newNode->next->prev = newNode;
// Increase number of nodes
dlist->currentCount++;
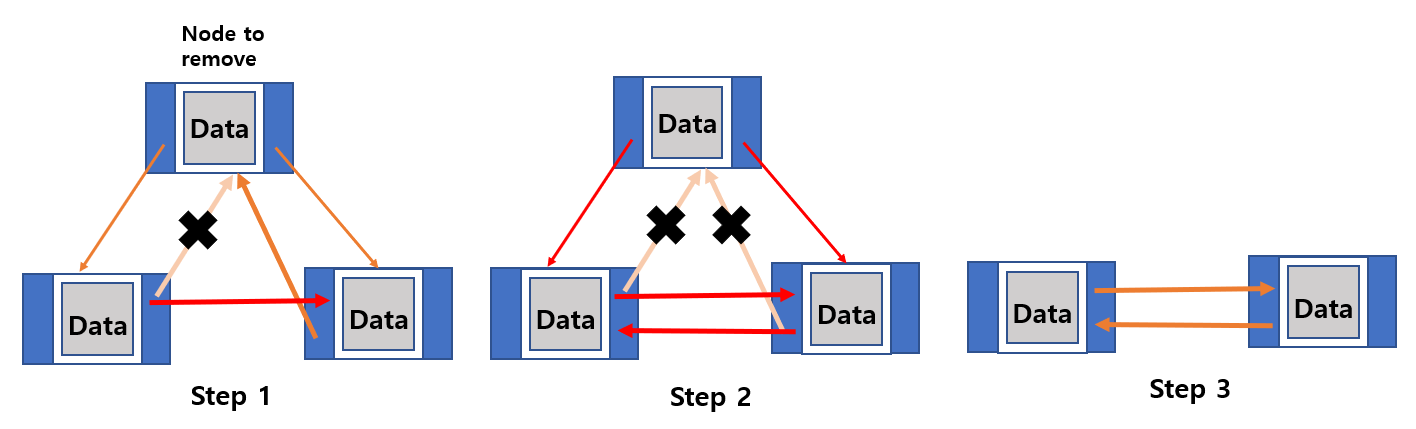
Remove node
- Find the position of the previous node you want to remove and reassign the ‘link of the prev node’ to the ‘next node’ of the ‘node you want to remove’.
- Free the memory of the node you want to delete.
// prevNode = Previous node of node to remove
prevNode = &(dlist->headerNode);
for (int i = 0; i < position; i++)
{
prevNode = prevNode->next;
}
// The previous node of delNode is prevNode
delNode = prevNode->next;
// The next node of prevNode is linked with the next node of delNode.
prevNode->next = delNode->next;
// The previous node of the next node of delNode becomes prevNode
delNode->next->prev = prevNode;
// Free the node to remove
free(delNode);
// Decrease number of nodes
dlist->currentCount--;