What is Circular Queue?
06 Jun 2020
Contents
Why use Circular Queue?
- Improve memory overflow of array queue
- Even if there’s a an empty node at the front, memory overflow occurs when we try to enqueue a new node.
- We can use the method of moving the array. However, beacuse the time complexity is O(N), it is a problem in a large array to move the array.
- Circular Queue is an efficient way to do this.
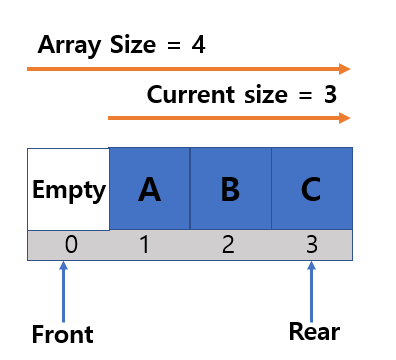
It is impossible to add a new node even if there is an empty node in Front.
To insert a new node into the Front, the existing nodes A, B, and C must be moved from 1, 2, 3 to 0, 1, 2.
But this process is not necessary in Circular Queue, because circular queue connect Front and Rear. To connect the front and rear, use mod operator to move the rear node.
Characteristic of Circular Queue
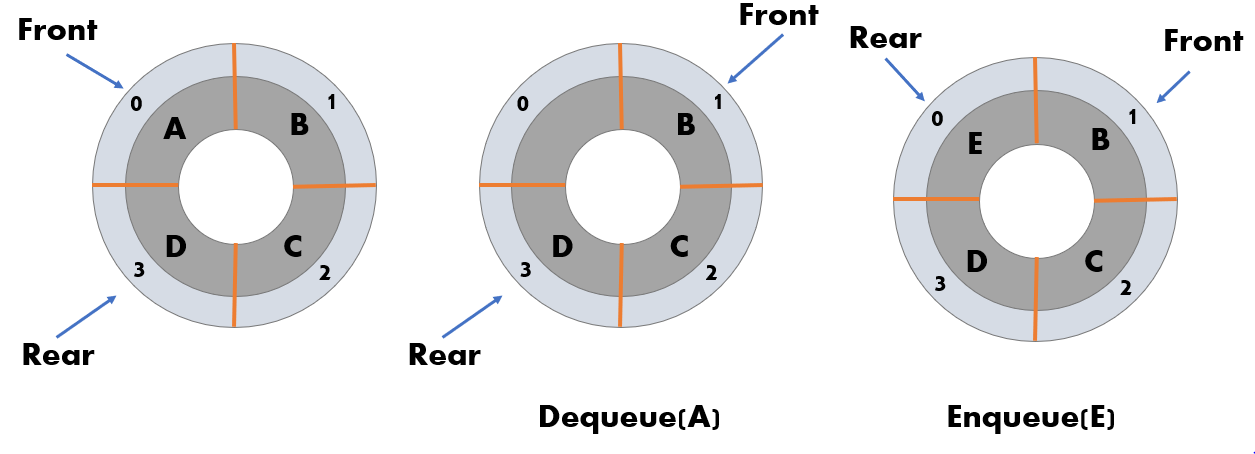
The basic operations are similar to Array Queue. The obvious difference is the location of the rear.
A is removed from index 0 by Dequeue(A), and then Front is changed to B in index 1. Then, Enqueue(E) inserts E into index 0 with empty node, and E becomes the new Rear.
rear = (rear + 1) % array size- rear = (3 + 1) / 4 =
0 - So, rear moved to
0
- rear = (3 + 1) / 4 =
Basic Operations
- First declare front and rear as
-1.rear = -1means array is empty.
enqueue
- Connect the
frontandrearof the array.- To connect the front and rear, use
modoperator to move the rear node. rear = (rear + 1) % array size
- To connect the front and rear, use
- If
rearis equal tomaxCount - 1, the queue is full.- maxCount is the maximum number of data that can be stored in an array.
// Change the position of rear
pQueue->rear = (pQueue->rear + 1) % pQueue->maxCount;
// Add new data
pQueue->pData[pQueue->rear].data = data;
// +1 number of node
pQueue->currentCount++;
dequeue
- Remove the node on the front and return it.
- Then, incresase the front by 1.
// Change the position of front.
// In Array Queue, pQueue->front++
pQueue->front = (pQueue->front + 1) % pQueue->maxCount;
// Store the data of node to be removed.
pReturn->data = pQueue->pData[pQueue->front].data;
// Decrease current number of data.
pQueue->currentCount--;
Peek
- Peek only returns the node in the front without removing it.
- Because the front was initially declared -1, the front + 1 location index must be used to return the data of the actual front node.
pReturn = &(queue->pData[queue->front + 1]);