What is a Heap?
14 Jun 2020
Contents
About data structure Heap
What is a heap ?
- Heap is a tree-based(
Complete binary tree) data structure. - Therefore, it is proper to implement a heap using array.
- The root node has the maximum or minimum value of the tree.
- Max heap if root node has the maximum value of tree.
- Min heap if root node has the minimum value of tree.
Types of heap
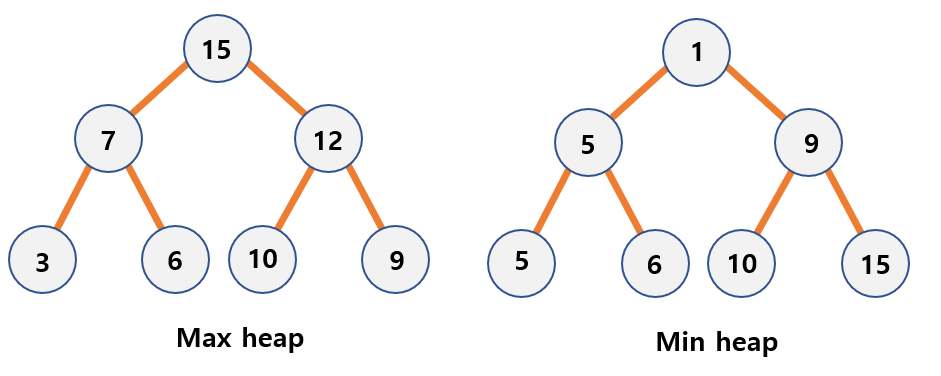
Max heap
Max heapis a tree that value for each node is greater than or equal to that of the child node.- Key value for parent node >= Key value for child node
- The root node’s key value = the maximum value of the tree
Min heap
Min heapis a tree that value for each node is smaller than or equal to that of the child node.- Key value for parent node <= key value for child node
- The root node’s key value = the minimum value of the ree
To be a tree that meets the conditions of the max and min heap, the tree must be a complete binary tree.
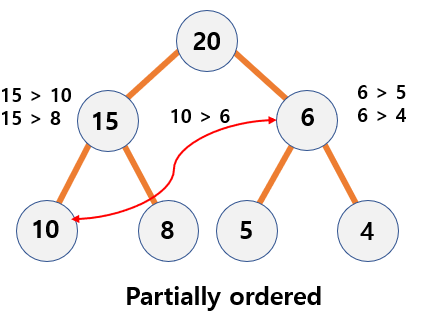
- Heap is a
partially ordered structure- For example, each node value is greather than or equal to the value of the child node in the max heap.
- However, each node is not greather than or equal to any lower level node.
Abstract data type of Array Heap
- Create a Heap
- Delete a Heap
- Add a data
- Remove a data
- The root node is removed and returned when data is removed from the heap.
- For the max heap, the next largest value becomes the new root node when the root node is removed.
- For the min heap, the next smallest value becomes the new root node when the root node is removed.
Heap requires two operations: Adding data and Removing data
Operations for Array Heap
Adding data
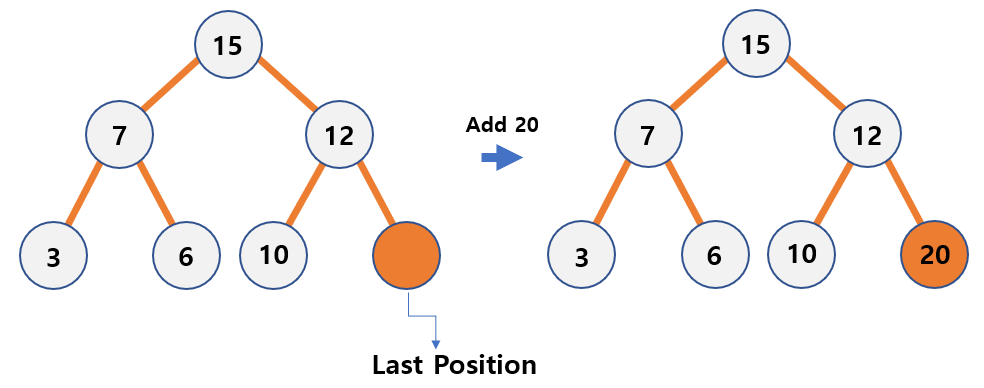
- When a new node is added to the heap, the new node is first
temporarily storedat the veryend of the tree. - Change the location of node
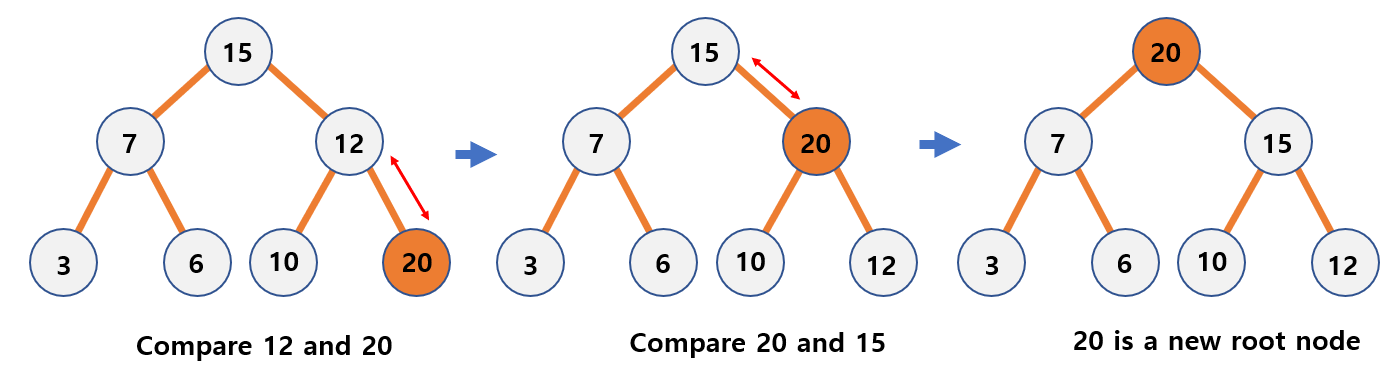
- Max heap: If the key value of a newly added node is greather than the key value of the parent node, the newly added node and parent node are repositioned. Repeat until the conditions of the max heap are met.
- Min heap: If the key value of a newly added node is less than the key value of the parent node, reposition the newly added node and the parent node. Repeat until minimum heap conditions are met.
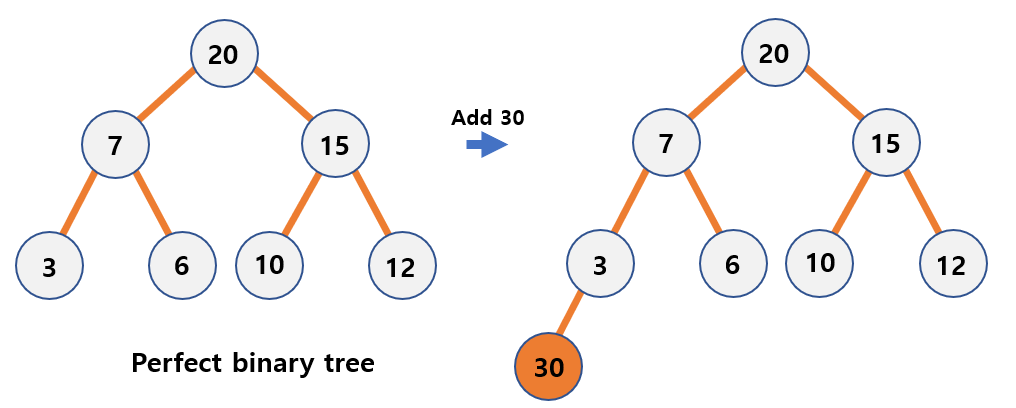
If the binary tree is a perfect binary tree, add a new level to add new data and add data to the far left of the new level.
Removing data
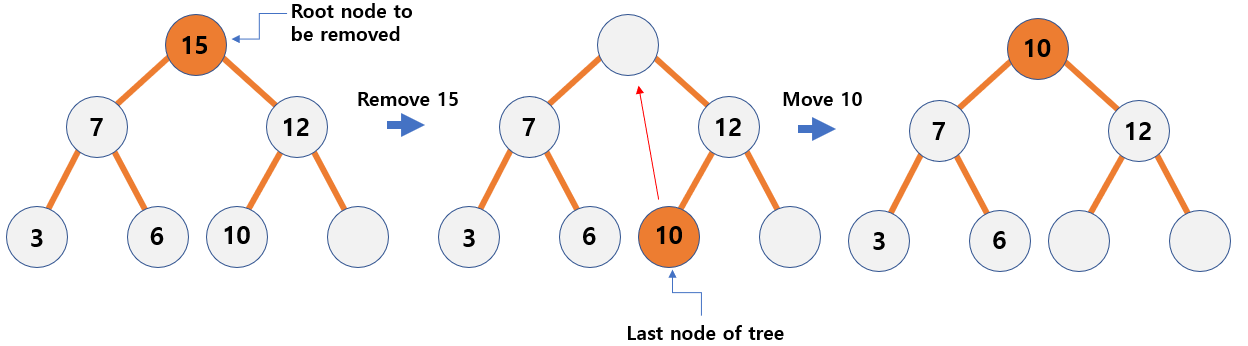
- Remove the root node.
- Max heap: The root node is the highest value
- Min heap: The root node is the lowest value
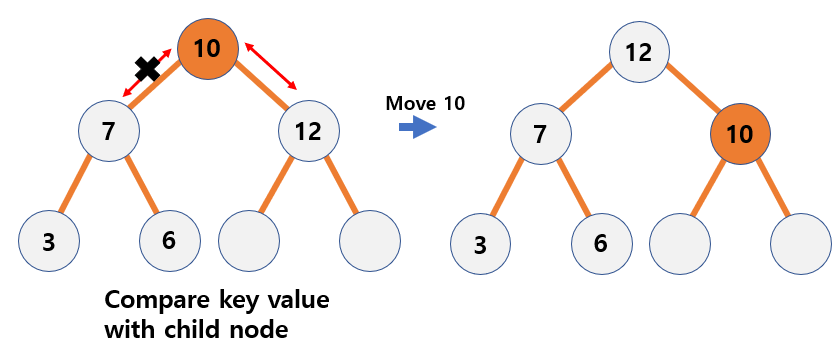
Temporarily move the last nodeof the tree to an empty root node.- Compare the value of the node to meet the conditions of the heap and change its position.