What is a Graph and types of Graphs
17 Jun 2020
Contents
About data structure Graph and its types
What is Graph?
- A graph is a
set of nodes and edges.- G =(V,E)
- Graphs are non-linear data structures.
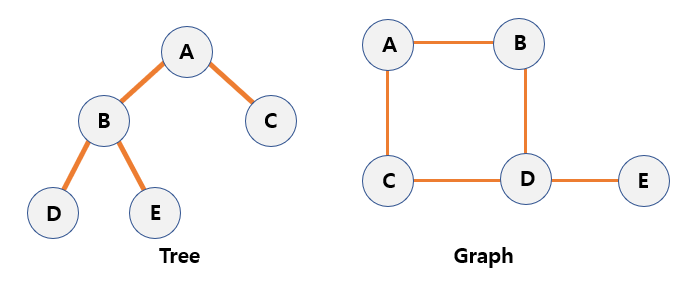
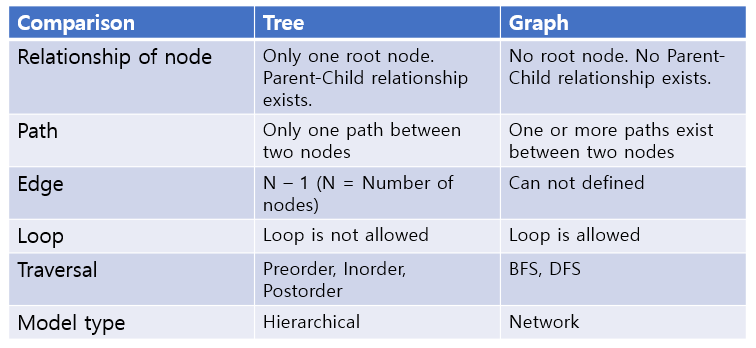
Difference between Tree and Graph
Characteristic of tree
- Root node exists
- The node except the root node is divided into subtrees.
- The tree extends downward.
- The tree must be connected.
- There is no loop.
Characteristic of graph
- The vertices on the graph can be connected to different vertices.
- You can set weights for the edge.
- Edges may or may not have direction.
Term of Graph
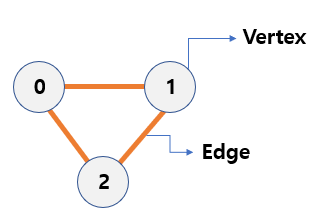
- Vertex - In the graph,
each noderepresents avertex. - Edge - Edge means a line that connects two vertices.
- Adjacency - If two vertices are connected through a edge, the two vertices are adjacent.
-
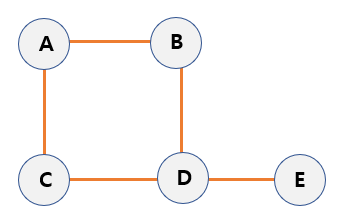
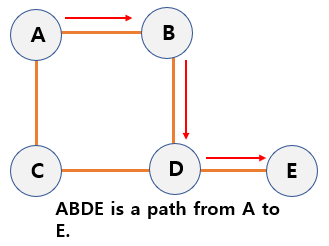
Path - The path is the
sequence of the edgesconnecting the two vertices.- Path length - The number of edges that consisting a path.
- Path length of ABDE = 3
- Simple path - If the nodes that consisting a path do not have the same node, it’s called a simple path.
- Cycle - If the starting node and the last node of the path are the same, it is called a cycle.
- Acyclic - Has no cycles.
- Path length - The number of edges that consisting a path.
- Degree -
The number of edgesconnected to the vertex.- In Directed graph
- In-degree - The number of edges entering the node.
- Out-degree - The number of edges leaving the node.
- In Directed graph
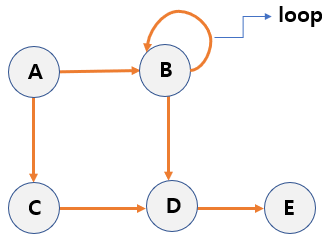
- Loop - When there is a
edge from a node to itself, it’s called a loop.
Types of Graphs
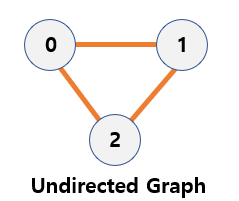
- Undirected graph
- Graph
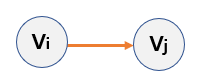
witout directoin on the edgesconnecting nodes. - We can move the two nodes in both directions.
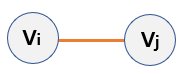
- The edge can be expressed in
(Vi,Vj)or(Vj,Vi).
- Graph
-
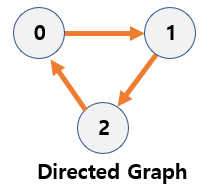
Directed graph
- Graph
with direction on the edgesconnecting nodes - It is only possible to move in a specific direction on both nodes.
- The edge can be expressed in (Vi,Vj).
- Graph
-
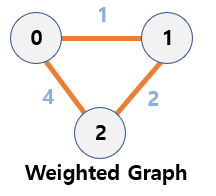
Weighted graph
- A graph
with weights on the edgesconnecting nodes. - It is also called a network.
- A graph
-
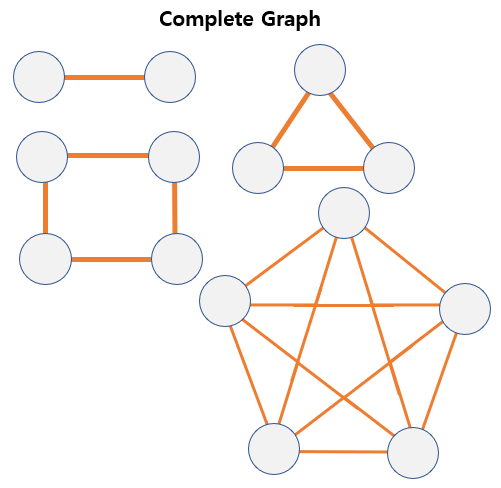
Complete graph
- A graph in which all vertices on a graph are connected
1:1. - All nodes are connected to each other, so there is
no edge to add. -
It has the
maximum number of connectable edges.- Max number of edges
- Undirected graph:
n(n-1) / 2, n = number of nodes. - Directed graph:
n(n-1)
- A graph in which all vertices on a graph are connected
-
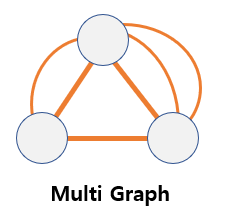
Multi graph
- Several edges are connected between the two vertices.
-
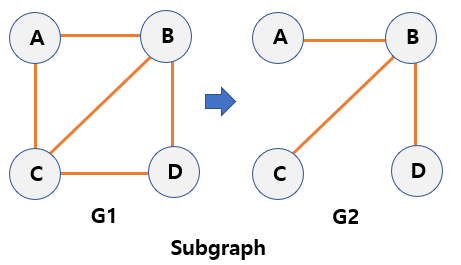
Sub-graph
- A graph created by excluding some edges from the original graph.
- A graph whose vertices and edges are subsets of original graph.
- G2 is a sub-graph of G1.
-
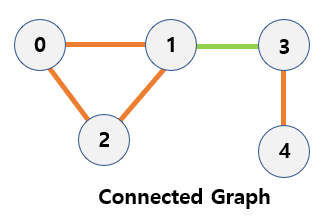
Connected graph
- A graph in which it’s possible to get from every vertex to every other vertex through edges.
-
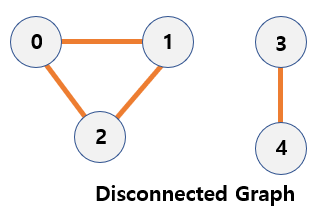
Disconnected graph
- If at least two vertices of the graph are not connected by a edge, it is a disconnected graph.